At first glance, optical fibers may seem like delicate strands of glass, but in reality, they are robust conduits for carrying beams of light encoded with immense volumes of information. Delving into the inner workings of these marvels reveals a complex interplay between principles of reflection and refraction that allows light to bounce within the fiber without losing its signal strength. As we peel back the layers of this technological wonder, we uncover a world where data zips through transparent pathways with minimal loss and maximum efficiency, laying the foundation for seamless connectivity on a global scale. Join us as we embark on an illuminating journey into the heart of optical fiber technology and unravel its secrets that have transformed our interconnected world.
Introduction: The Basics of Optical Fiber
Optical fiber is a fascinating technology that has revolutionized the way we transmit data. At its core, an optical fiber is composed of a thin strand of glass or plastic that serves as a waveguide for light to travel through. The principle behind its function lies in total internal reflection, where the light waves are continuously reflected within the core of the fiber, allowing for minimal signal loss over long distances. This design enables optical fibers to transmit vast amounts of data at incredibly high speeds, making them indispensable for modern telecommunications and internet infrastructure.
One key aspect of optical fiber is its ability to carry information in the form of light pulses, using different wavelengths to encode and transfer data. This feature gives optical fibers an immense capacity for bandwidth and allows multiple signals to be transmitted concurrently without interference. Furthermore, advancements in fiber optic technology have led to the development of specialized cables that can withstand extreme conditions such as underwater deployment and high-temperature environments, expanding their applications beyond traditional telecommunication networks.
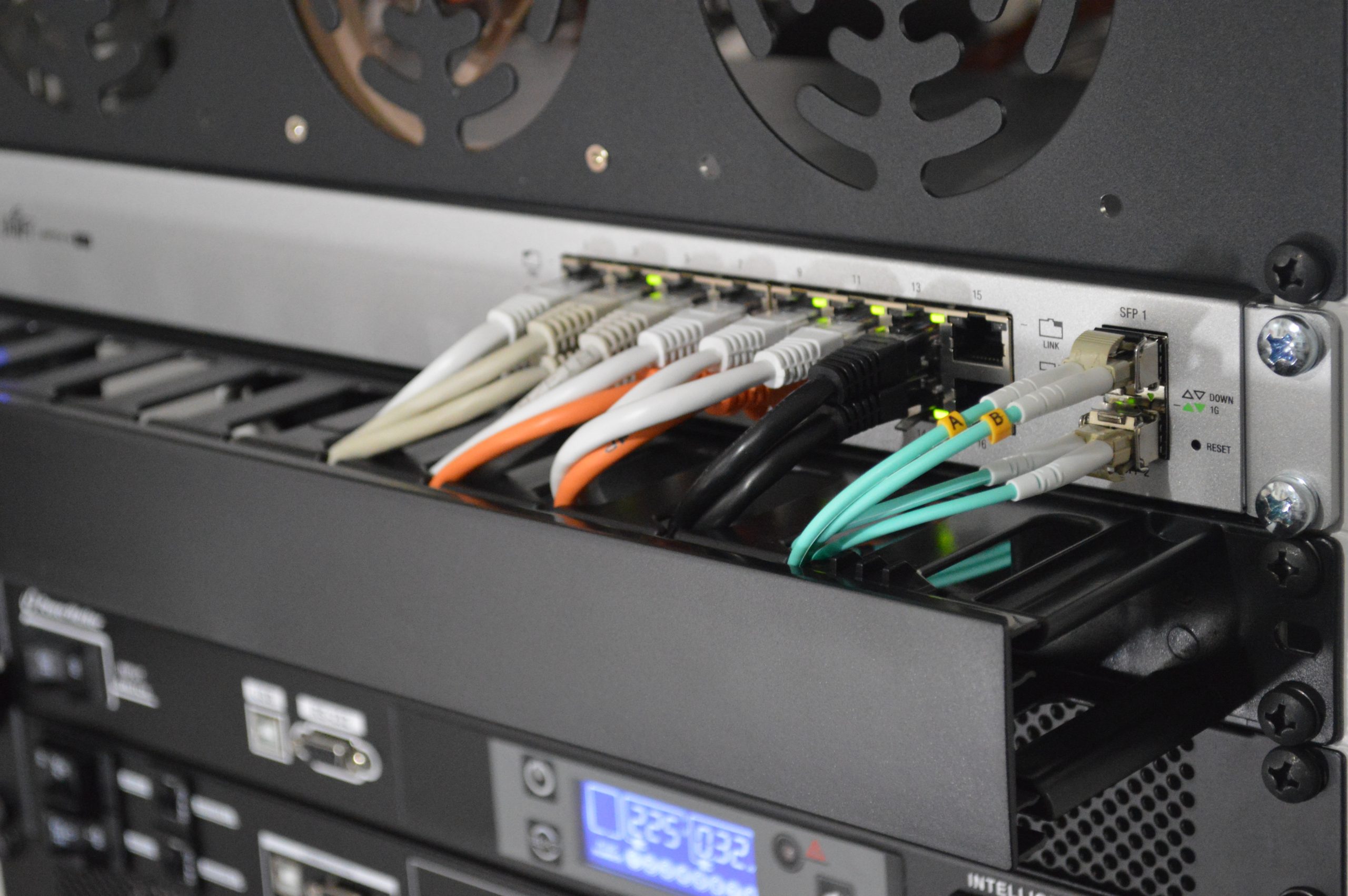

Structure: Composition and Design of Fiber
The structure, composition, and design of optical fiber are essential to its functionality and efficiency in transmitting data. Optical fibers are typically composed of a core made of high-purity silica glass surrounded by a cladding layer with a lower refractive index. This unique composition allows the fiber to transmit light over long distances with minimal loss. Additionally, the outer coating protects the fiber from environmental factors and physical damage.
The design of optical fiber is also crucial in maximizing its performance. Engineers carefully consider factors such as the core size, refractive index profile, and material purity when designing optical fibers for specific applications. By optimizing these parameters, engineers can enhance the bandwidth and transmission capabilities of optical fibers, making them ideal for various telecommunications and networking systems.
Transmission: Carrying Data through Light Signals
The transmission of data through light signals is a marvel of modern technology, revolutionizing the way information is carried across vast distances. By utilizing the principles of optics and the physics of light, optical fiber networks enable an astonishingly efficient means of communication. Unlike traditional copper wire systems, which rely on electrical signals to carry data, optical fibers use light signals that can travel over long distances with minimal loss of signal strength. This allows for faster and more reliable transmission of information, making it a crucial component in our interconnected world.
Furthermore, the use of light signals for data transmission provides several advantages over conventional methods. One key benefit is the significantly higher bandwidth capacity that optical fibers offer. This means that they can carry a much larger volume of data compared to traditional copper wires, making them essential for supporting today’s ever-increasing demand for high-speed internet and digital communications. Additionally, using light as the medium for data transmission decreases susceptibility to electromagnetic interference, providing a more secure and stable communication infrastructure. As technology continues to advance, the use of optical fiber networks will only become more prevalent as we strive towards even faster and more reliable connectivity.
In conclusion, understanding how data is transmitted through light signals via optical fiber sheds light on the intricate complexities behind our modern communication networks. The utilization of this technology not only provides astounding speed and reliability but also sets the stage for continued innovation in global connectivity. As we continue to push boundaries in digital information exchange, it becomes increasingly apparent that optical fibers are an indispensable component underpinning our

Advantages: Benefits of Optical Fiber Technology
The advantages of optical fiber technology are plentiful and impactful. Firstly, the incredible data transmission speed of optical fibers is unmatched by any other medium, allowing for rapid and efficient transfer of large amounts of data over long distances. This high-speed capability is particularly advantageous for businesses and industries that rely on real-time data processing, such as finance, telecommunications, and healthcare. Additionally, optical fibers are immune to electromagnetic interference, making them highly reliable in environments where electrical devices or heavy machinery may disrupt traditional communication methods.
Furthermore, the extensive bandwidth capacity of optical fiber technology enables it to accommodate a multitude of digital applications simultaneously without compromising performance. This makes it ideal for handling diverse multimedia services like streaming high-definition videos, conducting video conferences, and supporting cloud computing operations seamlessly. In essence, the benefits of optical fiber technology extend beyond mere connectivity; they empower businesses and individuals with a robust foundation for innovation and progress in our increasingly digital world.
Applications: Diverse Uses in Communication Networks
The potential applications of optical fibers in communication networks are boundless, ranging from traditional telecommunications to cutting-edge technologies. One significant use is in long-distance transmission, where fiber optics can carry vast amounts of data over great distances with minimal loss compared to traditional copper wire. This makes it ideal for global communication networks and has revolutionized the way we connect with each other across continents.
In addition, optical fibers are increasingly being utilized in high-speed internet connections, enabling faster and more reliable broadband services. The ability of fiber optic cables to transmit data at the speed of light has paved the way for advancements in telemedicine, video conferencing, and cloud computing. Furthermore, the advancement of optical networking technologies has enabled the development of 5G wireless networks which heavily rely on fiber optic backhaul to support ultra-low latency and high bandwidth demands. These diverse uses not only showcase the versatility of optical fibers but also push the boundaries of what is possible in modern communication networks.

Future Trends: Evolving Technologies and Innovations
In the ever-evolving world of technology, future trends promise to revolutionize the way we communicate, interact, and do business. One such trend is the advancement of quantum computing, which holds the potential to tackle complex problems at a pace never before seen. Additionally, artificial intelligence (AI) continues to expand its reach across various industries, offering advancements in automation and decision-making processes. Furthermore, the emergence of 5G networks promises unprecedented speed and connectivity for a wide range of applications.
As we look to the future, it’s evident that technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are poised to transform our everyday experiences. From immersive gaming and entertainment to practical applications in fields like healthcare and education, these innovations hold great promise for reshaping how we perceive and interact with our surroundings. Moreover, sustainable energy solutions are gaining momentum as the world seeks environmentally friendly alternatives. With breakthroughs in solar power technology and energy storage systems on the horizon, a cleaner and greener future seems increasingly achievable through technological advancements.
Conclusion: Impact and Potential of Optical Fiber
In conclusion, the impact of optical fiber in our modern world cannot be overstated. Its ability to transmit data at the speed of light has revolutionized communication, internet connectivity, and telecommunication networks. With its incredibly high bandwidth, low signal loss, and immunity to electromagnetic interference, optical fiber has become the backbone of global communication infrastructure.
Furthermore, the potential of optical fiber technology continues to expand as researchers push the boundaries of its capabilities. From advancements in long-distance transmission to developments in quantum communication, optical fiber is paving the way for future innovations in fields such as healthcare, transportation, and information technology. As we unlock new possibilities for harnessing light for data transmission and manipulation, the potential for even faster and more efficient communication systems becomes increasingly apparent. Optical fiber is not just a tool for today’s needs; it is a platform for shaping tomorrow’s technological landscape.