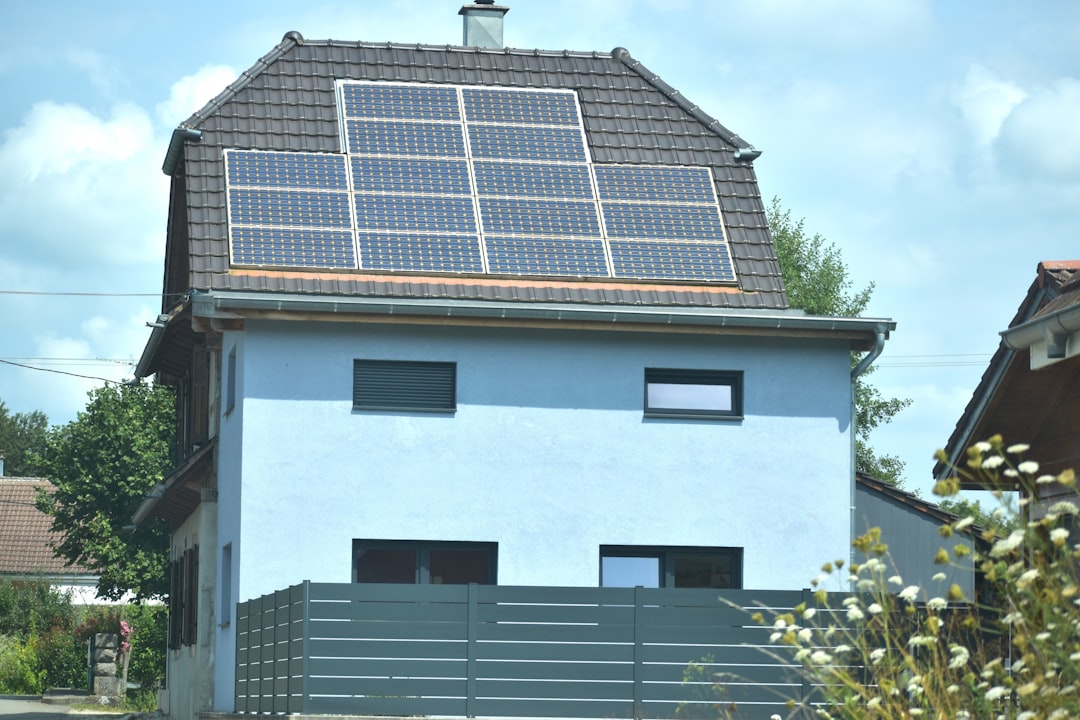
As climate change, rising energy costs, and rapid urbanization reshape how we live, integrating green technology into homes and cities has shifted from a niche idea to a practical necessity. Sustainable design is no longer just about protecting the environment; it also improves health, reduces long-term expenses, and makes communities more resilient. From energy-efficient homes to smart city infrastructure, green technology offers solutions that benefit individuals and entire urban ecosystems.
TLDR: Green technology can be successfully integrated into homes and cities through energy-efficient design, renewable energy systems, smart infrastructure, and eco-conscious transportation. These solutions reduce environmental impact while saving money and improving quality of life. Planning at both household and city levels is essential for long-term sustainability. The key is combining technology, design, and policy into one cohesive approach.
Why Green Technology Matters in Modern Living
Green technology focuses on reducing environmental harm while maintaining or improving efficiency and comfort. In home and city planning, this means lower emissions, reduced waste, smarter energy use, and healthier living spaces. Urban areas consume more than 75% of global energy and generate most greenhouse gas emissions, making cities a critical starting point for meaningful change.
When sustainability is built into planning rather than added later, it becomes more cost-effective and impactful. Green homes and cities don’t just benefit the planet; they provide better air quality, thermal comfort, and long-term economic value for residents.
Integrating Green Technology Into Home Design
Homes are the foundation of any city, and sustainable planning often begins at the household level. Modern green homes combine passive design principles with advanced technology.
1. Energy-Efficient Building Design
Well-designed homes can drastically reduce energy consumption before adding any technology. Passive strategies include:
- Optimizing window placement for natural light and airflow
- High-quality insulation to maintain indoor temperature
- Cool roofs and green roofs to reduce heat absorption
These features reduce reliance on heating and cooling systems, cutting both emissions and utility bills.

2. Renewable Energy Systems
One of the most visible ways to integrate green technology is through renewable energy. Solar panels remain the most popular option for homes due to falling costs and improved efficiency. Other alternatives include:
- Small-scale wind turbines in suitable locations
- Geothermal heating and cooling systems
- Solar water heaters
When combined with home battery storage, renewable systems allow households to store excess energy and reduce dependence on the grid.
3. Smart Home Technology
Smart systems make sustainability effortless. Thermostats, lighting, and appliances can now adjust automatically based on occupancy and usage patterns. Benefits include:
- Reduced electricity and water consumption
- Real-time energy monitoring
- Improved comfort without manual adjustments
Smart technology bridges the gap between human behavior and energy efficiency, turning everyday actions into sustainable habits.
Sustainable Materials and Water Management
The choice of materials and water systems plays a critical role in green home planning.
4. Eco-Friendly Building Materials
Using sustainable materials lowers the environmental footprint of construction. Popular options include:
- Recycled steel and reclaimed wood
- Bamboo and cork flooring
- Low-VOC paints and finishes
These materials often improve indoor air quality and durability while reducing waste and resource extraction.
5. Water Conservation Systems
Fresh water is a growing concern in many cities. Green homes address this through:
- Low-flow faucets and showerheads
- Graywater recycling systems
- Rainwater harvesting for landscaping and toilets
Water-efficient technology reduces strain on municipal supplies and supports long-term urban resilience.
Scaling Green Technology to City Planning
While individual homes matter, the true impact of green technology is felt when entire cities adopt sustainable planning strategies. Urban-scale solutions amplify environmental and economic benefits.

6. Smart Energy Grids
Smart grids use digital technology to manage electricity supply and demand more efficiently. They integrate renewable energy sources, reduce outages, and allow for dynamic pricing. Cities benefit from:
- Lower energy loss during transmission
- Faster response to demand changes
- Better integration of electric vehicles
Smart grids create a reliable backbone for sustainable urban growth.
7. Green Buildings and Zoning Policies
City governments play a vital role by encouraging or mandating green construction standards. Tools include:
- Energy-efficient building codes
- Incentives for green certifications
- Mixed-use zoning to reduce travel distances
Green zoning ensures sustainability is embedded in long-term development rather than treated as an optional upgrade.
Transportation and Public Spaces
Transportation and public infrastructure often contribute the largest share of urban emissions. Green technology offers ways to redesign these systems.
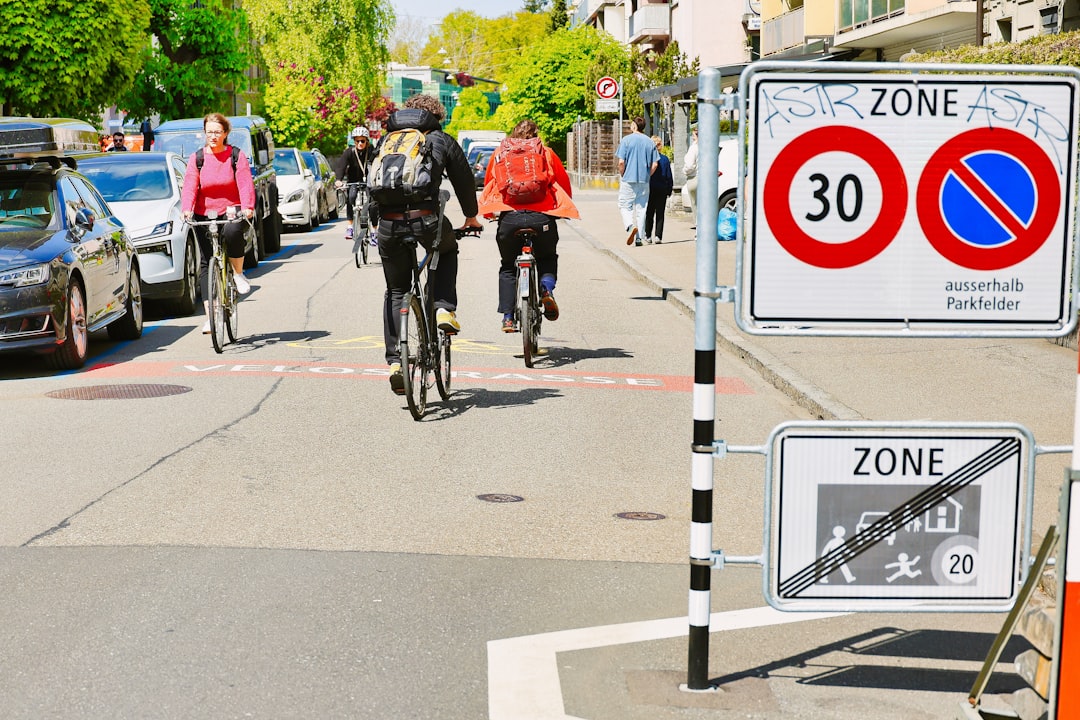
8. Sustainable Transportation Networks
Cities can reduce emissions and congestion by prioritizing:
- Electric buses and trains
- Protected bicycle lanes
- Pedestrian-friendly urban design
Supporting electric vehicle charging stations further accelerates the transition away from fossil fuels.

9. Green Public Spaces
Parks, urban forests, and green corridors are essential components of sustainable city planning. They:
- Reduce the urban heat island effect
- Improve mental and physical health
- Enhance biodiversity within cities
Strategically placed greenery also helps manage stormwater and improve air quality.
The Role of Data and Community Engagement
Technology alone is not enough. Successful integration of green solutions requires community involvement and data-driven decisions.
10. Using Data to Optimize Sustainability
Smart sensors and city dashboards collect data on energy use, traffic, and air quality. This information allows planners to:
- Identify inefficiencies
- Measure the impact of green initiatives
- Adjust policies based on real results
Data ensures sustainability efforts are transparent and continuously improving.
11. Educating and Empowering Citizens
Public awareness is crucial. Cities and homeowners benefit when residents understand how to use green technology effectively. Workshops, incentives, and clear communication help people:
- Adopt energy-saving behaviors
- Support long-term sustainability goals
- Feel invested in their environment
Looking Ahead: Building a Greener Future
Integrating green technology into home and city planning is not a single solution but a comprehensive, evolving strategy. From smart homes and renewable energy to public transportation and green spaces, sustainability thrives when technology, design, and policy align.
As innovation continues and costs decrease, green solutions will become more accessible to cities of all sizes. By planning today with environmental responsibility in mind, we create homes and cities that are healthier, more efficient, and better prepared for the challenges of tomorrow.